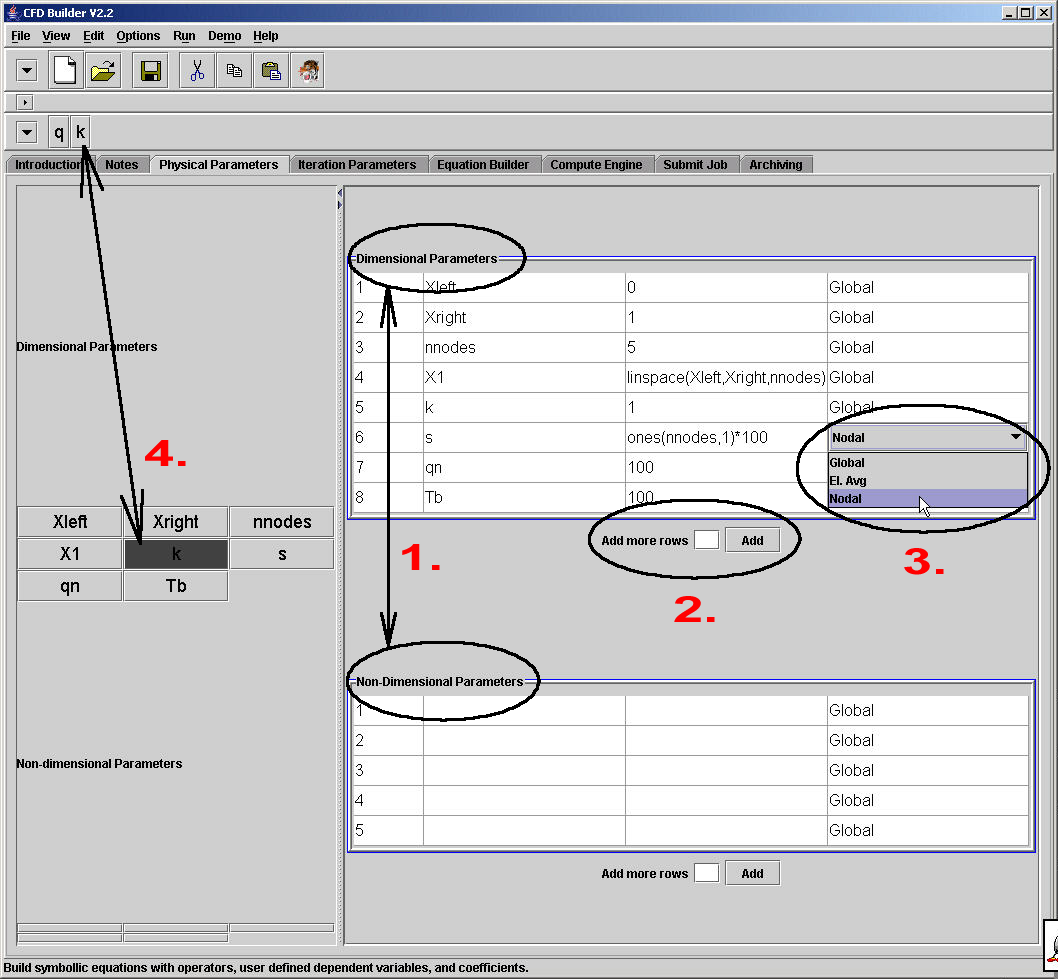
Figure 1. "Physical Parameters" panel
Physical Parameters Panel
The "Physical Parameters" panel contains problem specific parameters such as density, viscosity, Reynolds number, and so on (Figure 1).
1. Data is divided in two categories: dimensional and non-dimensional. There are no checks to ensure that the data is truely dimensional or non-dimensional. The separation is a visual aid only designed to help the user in book-keeping this important issue.
2. If there are not enough rows to enter data, put an integer value of how many more rows of data you need at "Add more rows" and press the "Add" button. This may be done as many times as required without loosing the original data.
The tables contain 4 columns for data. The first column is an uneditable index number column. The second column is the Parameter variable or name. These variables may be symbollic and are translated into text script via the Program Variables, as described in the Toolbars help documents. When instruction or errors are given about "Constants", "coefficients", or "known data", it is this Parameter Name that is being referred to. The third column is the Parameter value. This is the value that the Parameter Name will take (i.e. k = 1, parameter name = parameter value). This column is typically "literal", meaning that whatever is put in this column shows up in the compute engine EXACTLY as specified.
3. The last column title "Data Type" specifies what kind of data this parameter represents. If the parameter does not show up in the equations then this will probably not be used. Otherwise, the compute engine must know if this information is a constant over the entire domain, element averaged, or is applied to the nodes in the domain. Matlab compute engine errors occur due to an incorrect data type specification more often than any other cause.
4. Notice to the left of the Physical Parameters panel that buttons are created as the Parameter Names are defined. These buttons are not used to build equations in this pane, but rather pressing a button will send that button to the Variable Toolbar for use in building equations and Jacobians. Not all parameters need to be sent to the toolbar, and parameters may be removed from the toolbar by pressing the left panel button a second time.

Figure 1. "Physical Parameters" panel